“The Steinheim impact crater (SW Germany) – where are the ejecta?” – title of an extended paper by Buchner and Schmieder to be published 2015 in Icarus.]
At the this year’s 77th annual meeting of the Meteoritical Society Buchner & Schmieder (2014) have presented an abstract article about the apparently missing impact ejecta of the Steinheim impact crater (Steinheim Basin). Starting point is the statement that beyond of the impact basin not any ejecta are known in obvious contrast to the distinct ejecta curtain of the same-aged, however much larger Ries impact crater.
On the one hand, a primary effect – practically no ejecta were produced upon impact – is discussed, and on the other hand the possibility of a complete erosion of originally existing ejecta is considered. Because of the today’s distribution of the post-impact Miocene sediments around the Steinheim Basin the second possibility is thought to be little likely, and instead a primary effect is favored.
The postulated primary absence of excavation and ejection upon the Steinheim Basin formation is related by the authors with a paper written by Housen & Holsapple (2012; similar papers of these authors also earlier). In this article ejection mechanisms for craters on strongly porous bodies in the Solar System are discussed with the result that on those bodies big craters do not feature impact ejecta in contrast to less porous bodies. The idea is substantiated by laboratory experiments and scaling laws which are obviously compatible with observations of e.g., the Mathilde asteroid (≈ 50% porosity) and the Saturn moon Hyperion (≈ 40% porosity) where the big craters don’t possess significant impact ejecta, but smaller craters however. According to that (Fig. 6 in Housen & Holsapple 2012), a very rough threshold is given by craters with diameters 20 – 50 km and with target body porosities of > 40% assuming that gravity on the highly porous body is not an issue. In the end and a bit simplifying, the reason for a prevention of ejection is the extremely porous material that in the excavation stage and with the development of the transient crater (see here: … understanding the impact cratering process – a simple approach) is preferentially compressed downwards and towards the sidewalls. Hence, percentally much less rock material can find its way outwards in large craters in contrast to smaller ones.
This model is applied by Buchner & Schmieder (2014) to explain the seemingly missing impact ejecta around the Steinheim Basin.
We discuss:
1 The crater size of the Steinheim Basin
Commonly, a diameter of 3.8 km (also 3.7 km) is ascribed to the Steinheim Basin. A gravity survey and a detailed morphological analysis reveals however that this impact structure probably is much larger. Thus, a diameter of 6-7 km seems to be realistic as is shown in the paper by Ernstson (1984: A gravity-derived model for the Steinheim impact structure. International J. Earth Sci. , 73/2, 483-498) and is evident in Figs. 1, 4 and Fig. 5.
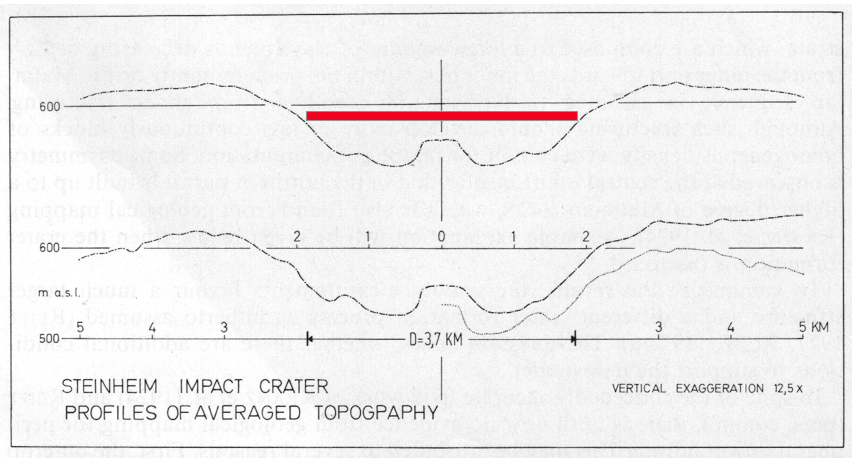
Fig. 1. Profile of Steinheim Basin averaged topography (from Ernstson 1984). Upper profile: topography from 32 averaged radial profiles. Bottom profile: topography from 16 averaged southern profiles (to the left) and 16 averaged northern profiles (to the right). Dashed line: left profile (south) mirrored at the zero axis and 20 m shifted. The 3.7 km bar (red) represents the mean diameter of the crater as it is kept used in the literature obviously not corresponding to reality.
Although this article has been printed in an internationally renowned journal, even in more recent papers on impact modeling of the Steinheim Basin (Stöffler et al. 2002, Ivanov & Stöffler 2005) the small diameter is further on used making the results of these crater models rather suspect (see a respective discussion HERE). Such is the case with the Buchner & Schmieder (2014) article who use a 3.8 km diameter but withhold and do not refer to the alternative of the significantly larger crater. Like with Stöffler and Ivanov this must be called bad scientific style (omitting quotation) and dubious scientific working using wrong preconditions as potential starting point.
2 Possible erosion of the ejecta
— Because of the extended forests (Fig. 2) a reliable mapping in the surroundings of the Steinheim Basin is problematic. Buchner & Schmieder don’t write what kind of mapping, to what extent and on what a scale was performed.
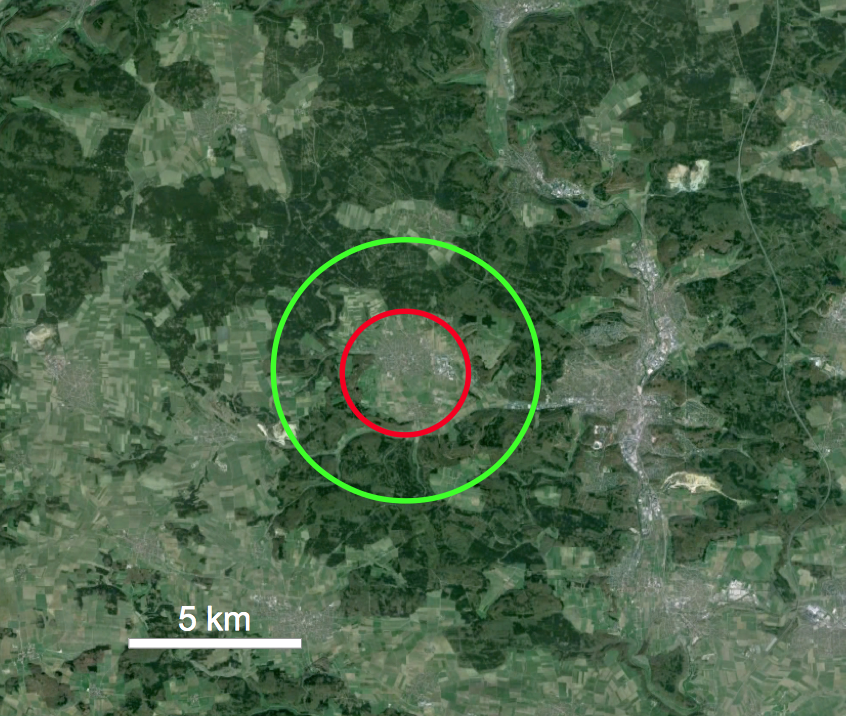
Fig. 2. The Steinheim Basin within large forested areas. Red: conventional diameter (3.7 km, resp. 3.8 km); green: diameter according to Ernstson (1984). Google Earth.
— Paleogene and Miocene deposits that are quoted by Buchner & Schmieder to show that ejecta would probably have survived are not found in the geological maps (Kranz 1923, Gediga 1984, Reiff 2004).
— Loamy layers with silifications widespread to be mapped on the Alb plateau and also bordering the Steinheim Basin (see geologic map) may well be relics of weathered Malmian ejected limestones.
— The today’s morphology in the surroundings of the Steinheim Basin featuring deeply cut dry valleys (Fig. 3) prove significant erosion.
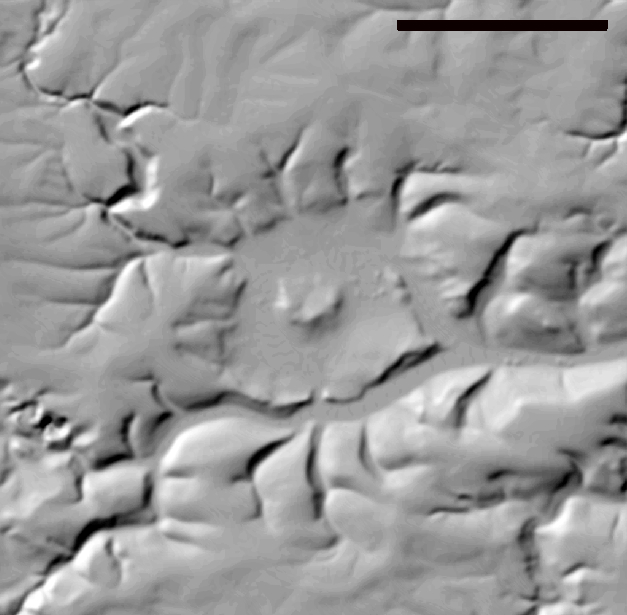

Fig. 3. Relief map of the Steinheim Basin. Scale bar 3 km. (Source: TOP25 Baden Württemberg).
— The erosion of an originally existing rim wall is explicitly mentioned in Reiff (2002, Fig. 84). In the image sequence 1 – 8 of the basin development phase 2 shows the crater immediately after the impact having a distinct rim wall which by erosion becomes smaller and smaller. For phase 7 – Pliocene – we read: “The rim wall is leveled”. This has been written by W. Reiff, probably the best expert for the more recent geologic research in the Steinheim Basin. I.e., independently of the true, larger or smaller crater size Reiff assumes a significant post-impact erosion (phase 6: tectonic uplift of the Alb mountains) that let the rim wall with the biggest ejecta thickness disappear completely. Also the more distant ejecta with strongly decreasing thickness should not have escaped this erosion. This is not circular reasoning: Reiff does not postulate erosion because of the lacking rim wall (according to Buchner & Schmieder a primary feature) but instead he refers to the post-impact Earth history in the region implying significant erosion also in the Ries impact structure and its surroundings.
— Independently of the post-impact erosion history and the disappearance of the ejecta postulated by Reiff, the morphological analysis addressed above under 1 (Ernstson 1984) shows that a circular rampart of the significantly larger crater seems to exist still today.
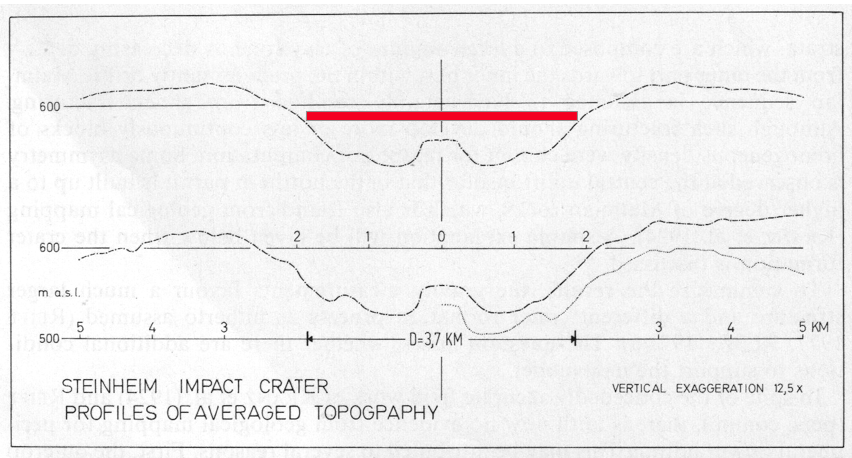
Fig. 4. Profiles of averaged topography taken from the Steinheim impact basin (from Ernstson 1984). Explanation see Fig. 1)
Conclusions on 2: The assumption that from the beginning a ejecta curtain did not exist has not any convincing base; Buchner & Schmieder don’t supply the reader with scientific proof. Ejecta and/or their weathering relics may exist still today or/and underwent erosion.
3 The Housen & Holsapple (2012) hypothesis
— The hypothesis differentiates between small and big craters on bodies in the Solar System, where according to a high porosity ejecta curtains do develop or not, respectively. In this sense Steinheim is a small crater (be it the old 3.8 km, be it the 6-7 km postulated by Ernstson (1984)); the threshold is 20 – 50 km after Housen & Holsapple.
— The porosity: Housen & Holsapple postulate a porosity of more than ≈40% in order the process of ejecta formation is suppressed. Buchner & Schmieder quote porosities between ≈21% and ≈44% for the target rocks of the Steinheim Basin and reason these figures with an intense karstification of the Malmian limestones and dolomites. For the whole target they even prefer the larger value of ≈44% porosity. It’s a mystery where these unbelievably high porosity values with a yet certain precision (21, 44) for the sedimentary sequence of the Swabian Alb during the Upper Miocene some 15 Mill years ago originate from. A reference does not exist.
— Investigations especially in more recent deep geothermal boreholes revealed intergranular porosities of Malmian limestones and dolomites near 3.5 %, partly < 3%. Assuming a bulk porosity, karst cavities included, of up to ≈44 % this means that one third or more of the rock volume must be cavernous (open joints, karst cavities). With regard to the innumerable large quarries cut into the Malmian of the Alb it remains enigmatic how Buchner & Schmieder arrived at these porosities.
— It is possibly to convert porosities into densities using, e.g., plausible 2.6 g/cm³ as matrix density for the Malmian limestones. Then, a porosity of 44% is related with a Malmian bulk density of about 1.9 g/cm³ if the whole pore volume is filled with water. Applied to about 150 m dry rocks above the on-site preflooder the density reduces to only c. 1.45 g/cm³. The latter is a little more than the density of the 50 km-diameter Mathilde asteroid (1.3 g/cm³) which is considered a rubble pile body. And exactly for that reason Mathilde was used by Housen & Holsapple to test their models and scaling laws (see above).
But the Steinheim Basin underground? Every geophysicist’s hair would stand on end when, conducting a gravity survey in the Alb mountains, he/she should do his/her mass correction using a reduction density of 1.45 g/cm³ with the consequence that his/her gravity map would practically be the mirror image of topography.
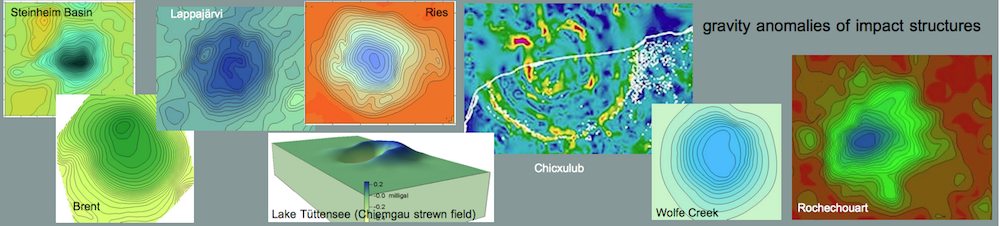
Moreover, given the Housen & Holsapple model is applicable to the Steinheim crater, then after the impact the basin underground density should have increased compared with the surroundings, due to the strong shock compression downwards and sidewards squeezing the karst fissures and cavities. Hence, a gravity survey today should measure a positive gravity anomaly over the crater. This is evidently not the case as a reasonable density model proves (Fig. 5).
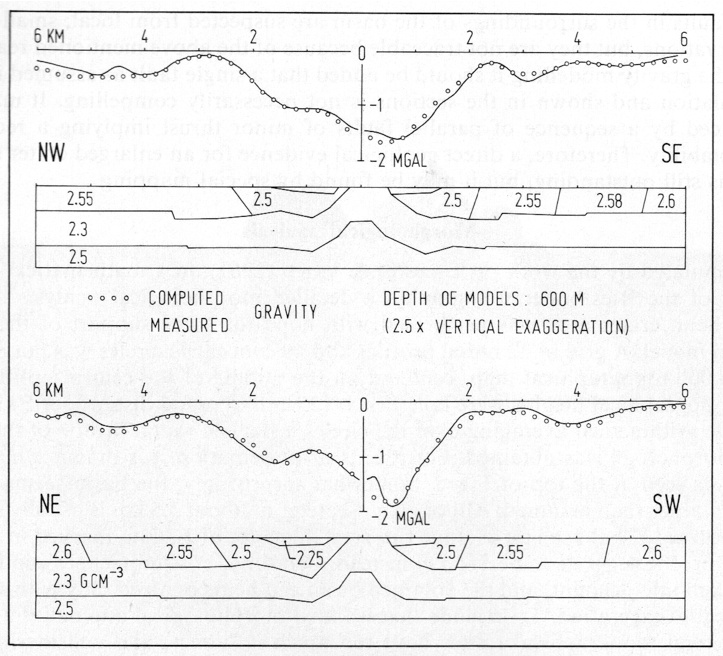
Fig. 5. Results of gravity modeling for the Steinheim impact basin. Densities are g/cm³. (from Ernstson 1984).
Conclusions on 3: The starting point of Buchner & Schmieder to apply the Housen & Holsapple model to the Steinheim impact crater is far from any geologic and geophysical reality und thus in the end leads to nothing.
General conclusions
In principle it is reasonable and in science the appropriate line to make observations, carry out experiments and analyses before (!) calculations and computer modeling are considered and performed to support explanatory models or to disprove them. However, more recently it can be stated more and more frequently that the cart is put before the horse, which means the computer models are put at the very beginning and the observation (in geology the field work) has to be kindly adapted.
Seemingly Buchner & Schmieder chose the correct way: In the first place the observation of the apparently non-existing ejecta at the Steinheim Basin and then the theoretical model that should explain the observation. However, in the end they were thinking nothing else but the model in order to make the observations fit the model: disregarding the literature of most experienced geologists (e.g., Reiff 2002), ignoring important articles about the Steinheim impact crater (Ernstson 1984), not involving specifications of the theoretical model (contrasting big and small craters with distinct differences), disregarding existing geophysical data (the negative gravity anomaly), and finally – scientifically especially inexcusable – to present parameters (absolutely unrealistic porosities for the Steinheim underground rocks) without any source.
Once again, Buchner & Schmieder demonstrate that by hook or by crook they want to give the Steinheim Basin a particular importance that does not exist, and we mention their paper on the Steinheim “suevite” that can be shown is a pure fiction. (see a comment on that article)
References
Buchner, E. & Schmieder, M. (2010): Steinheim suevite – A first report of melt-bearing impactites from the Steinheim Basin (SW Germany). -Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 45, 1093-1107. (comment on the article)
Buchner, E. & Schmieder, M. 2014): The Steinheim impact crater (Germany) – where is the ejecta blanket? – 77th Annual Meteoritical Society Meeting, 5168.pdf.
Ernstson, K. (1984): A gravity-derived model for the Steinheim impact structure. International J. Earth Sci. , 73/2, 483-498).
Ernstson, K., Mayer, W., Neumair, A., Rappenglück, B., Rappenglück, M.A., Sudhaus, D. and Zeller, K.W. (2010): The Chiemgau crater strewn field: evidence of a Holocene large impact in southeast Bavaria, Germany. – Journal of Siberian Federal University, Engineering & Technology, 1 (2010 3) 72-103.
Gediga, P. (1984): Geologische Karte von Steinheim 1 : 10 000, Diploma thesis Universität Essen.
Housen, K.R. & Holsapple, K.A. (2012): Craters without ejecta. – Icarus, 219, 297-306.
Ivanov, B.A. & Stöffler, D. (2005): The Steinheim impact crater, Germany: Modeling of a complex crater with central uplift. -Lunar and Planetary Science XXXVI (2005), 1443.pdf.
Reiff, W. (2002): Das Steinheimer Becken, Darstellung der geologischen Zusammenhänge (Teil I), in: Heizmann, E.P.J. & Reiff, W.: Der Steinheimer Meteorkrater (Gemeinde Steinheim, Hg.), Pfeil-Verlag, München, 160 S.
Stöffler, D., Artemieva, N.A. and Pierazzo, E. (2002): Modeling the Ries-Steinheim impact event and the formation of the moldavite strewn field. -Lunar and Planetary Science XXXIII (2002) 1871.pdf.




















































 Dr. Lynn B. Lundberg
Dr. Lynn B. Lundberg A new book has recently been published:
A new book has recently been published: