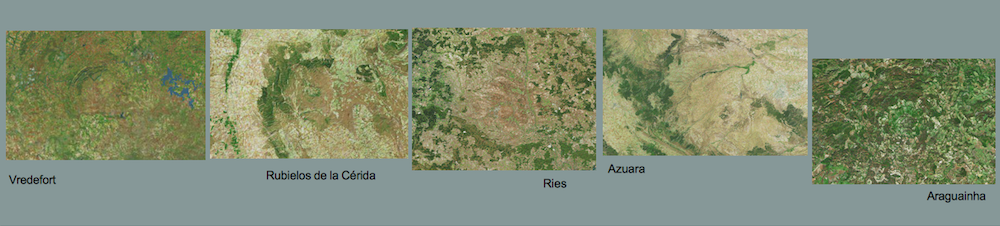
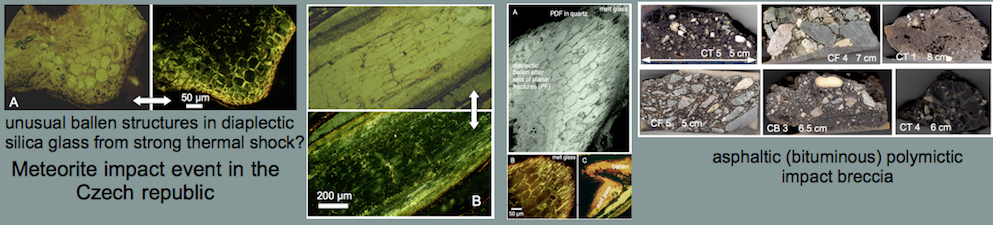
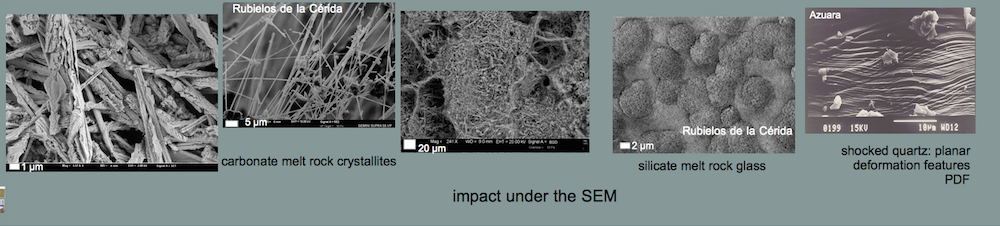
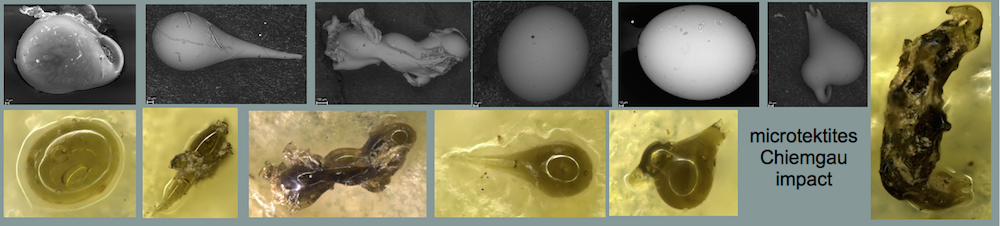
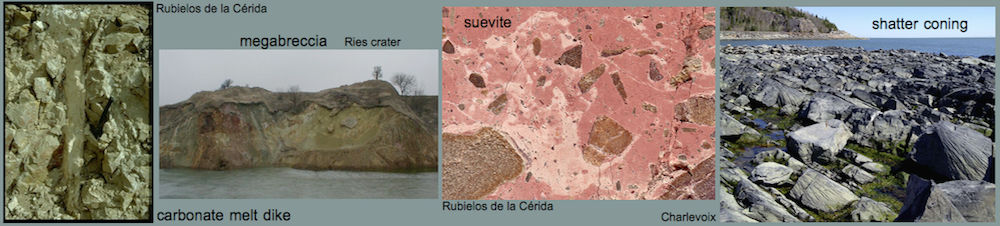
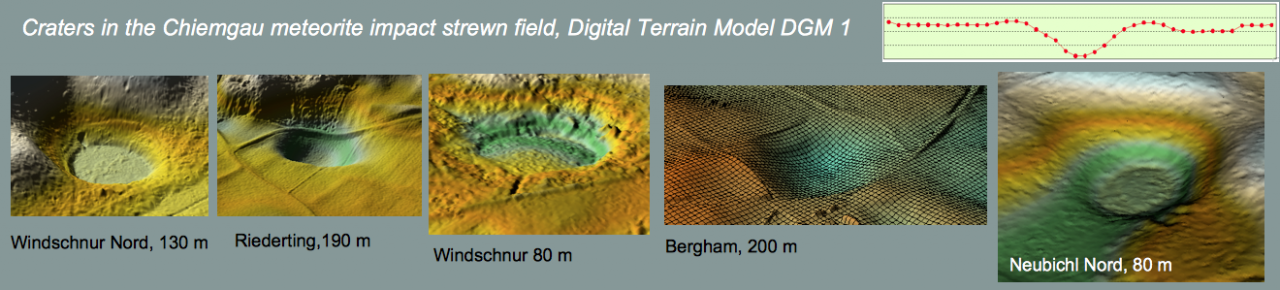
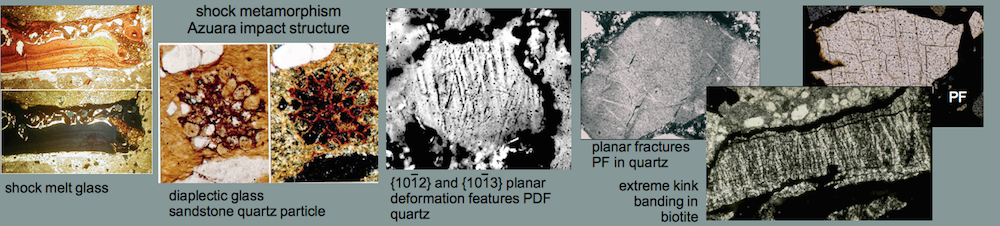
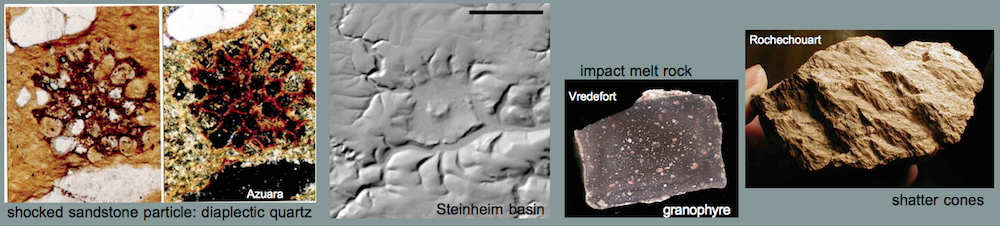
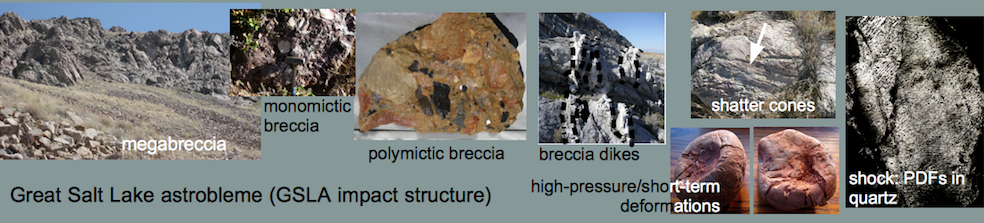
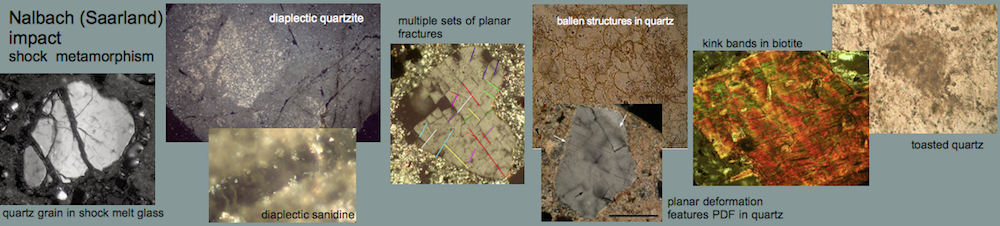
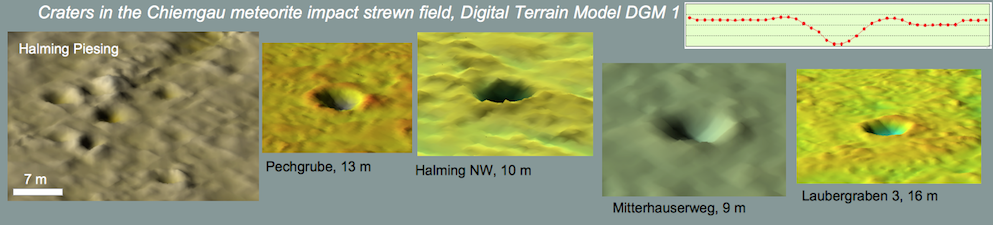
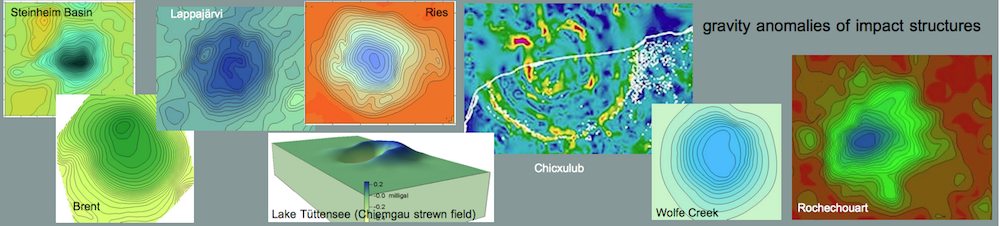
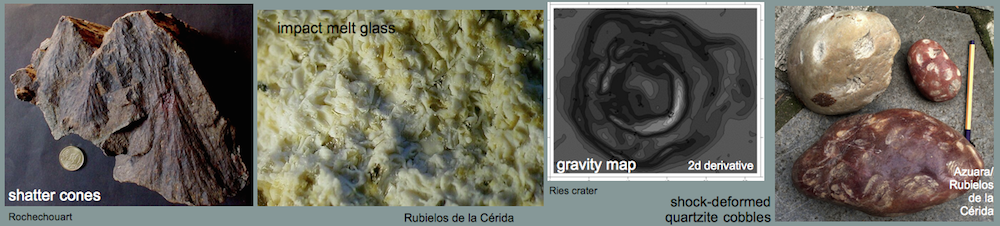
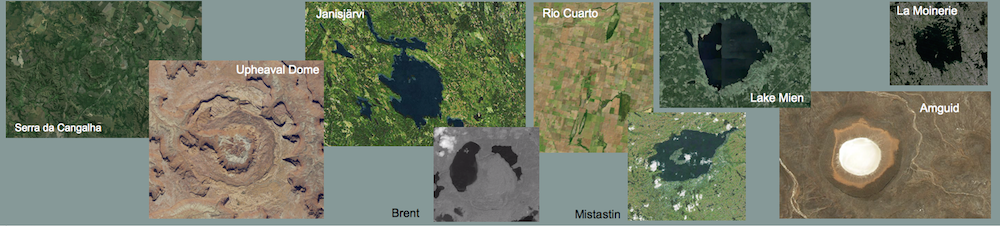
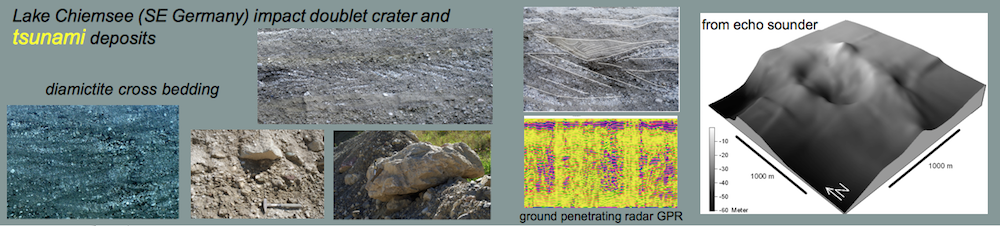
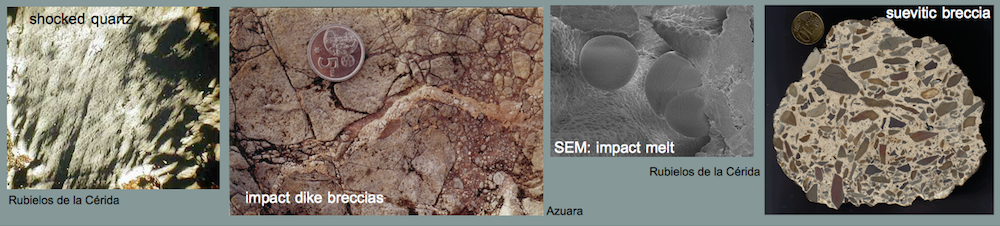
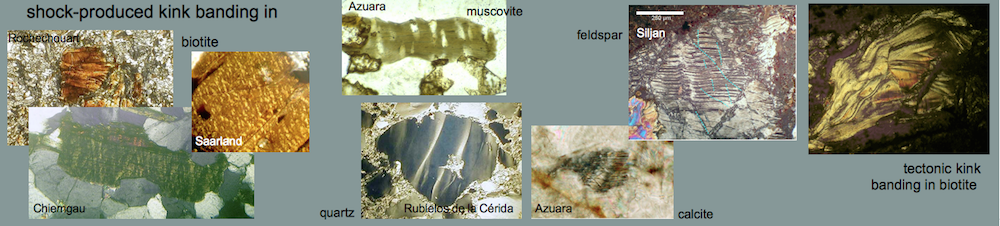
Shock effects in the Nördlinger Ries crater are mostly concentrated to the suevite wherein all stages of shock from unshocked to shock melt can be observed.
A few typical examples are shown below .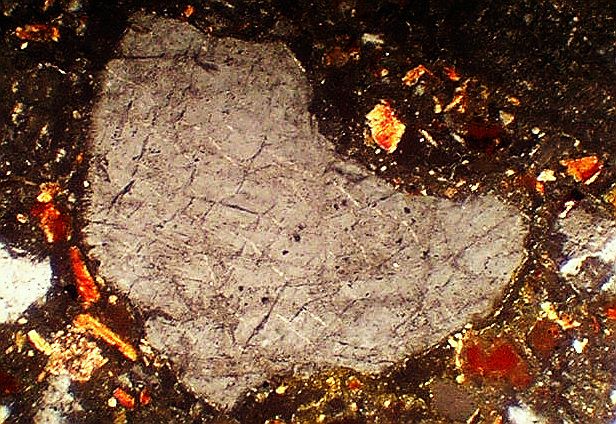  Fig. 1. Multiple sets of planar fractures (cleavage) in quartz; suevite breccia. Width of photomicrograph 600 µm.
Fig. 1. Multiple sets of planar fractures (cleavage) in quartz; suevite breccia. Width of photomicrograph 600 µm.

Fig. 2. Planar deformation features (PDF) in quartz grain. Width of image 460 µm.
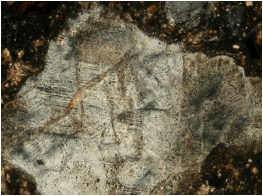
Fig. 3. More PDFs in quartz; suevite.
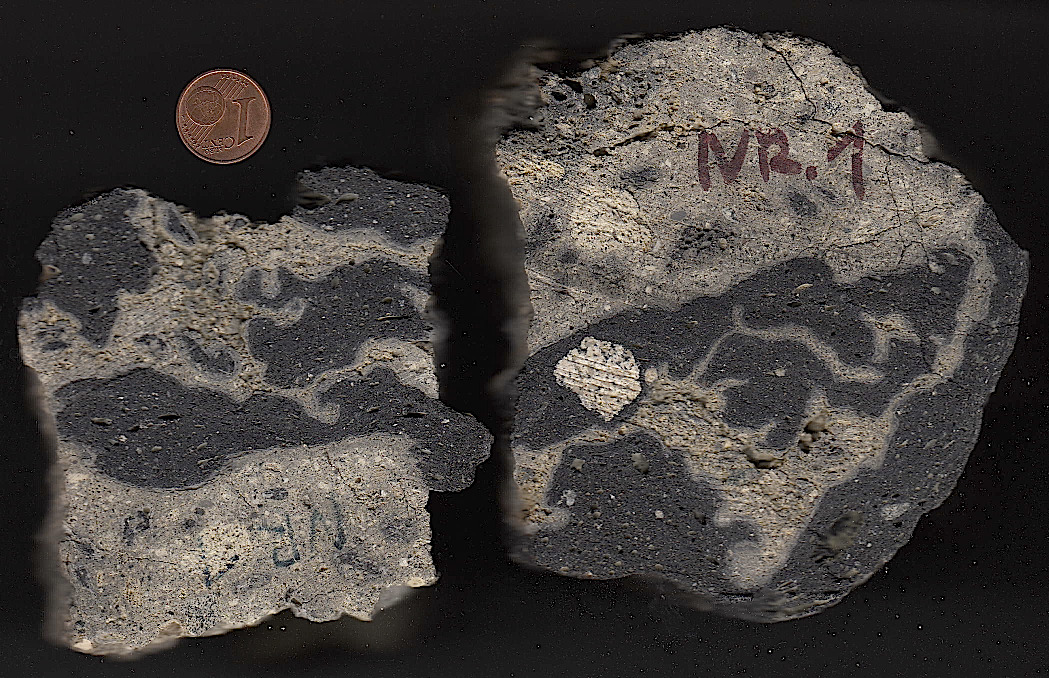
Fig.4. Highest shock level: total-rock melt (black glass) in a suevite sample.
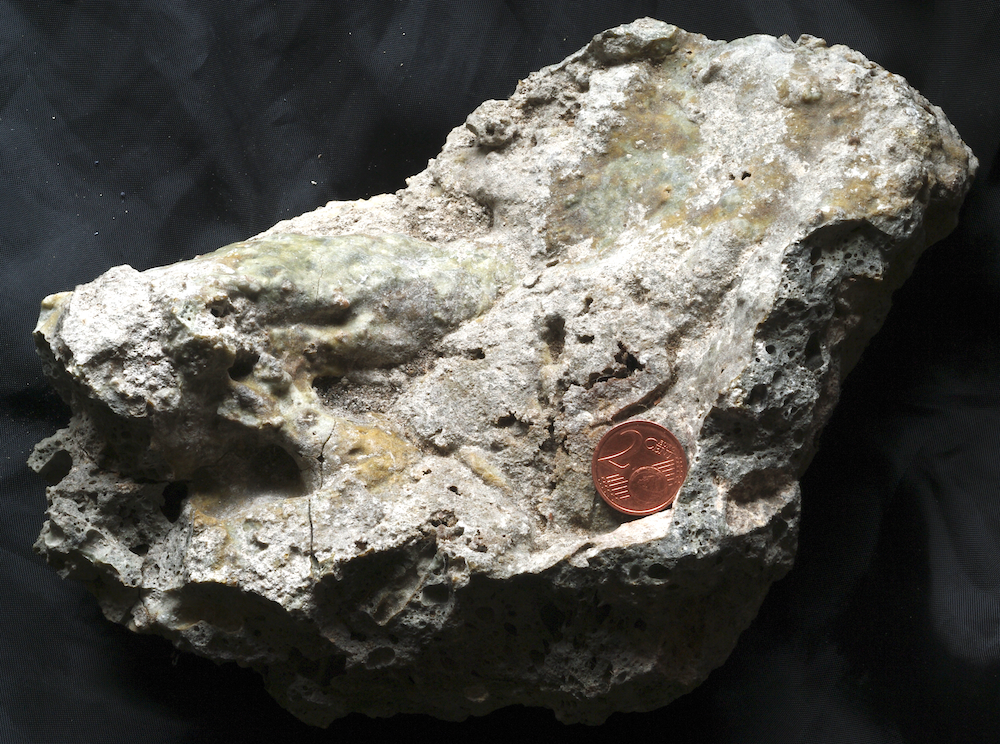

Fig. 5. More shock-melted rock; glass chunk weathered from a suevite.